Elivepatch
Sponsor[edit | edit source]
Tokyo University of Technology - server sponsor
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Flexible Distributed Linux Kernel Live Patching
livepatch is a Linux kernel facility that allows to build a kernel module to update a running kernel without requiring a reboot.
Elivepatch is a client-server infrastructure to automate the creation and distribution of those modules.
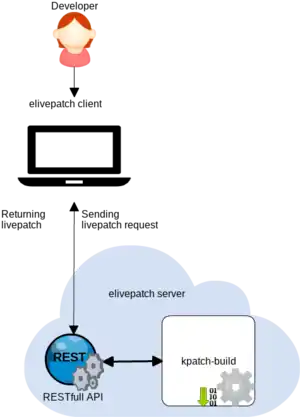
Use cases[edit | edit source]
- Resource-constrained updates
- Distributed live patch building
- Incremental live patch (You can build live patch over the previous one)
- Automatic no-reboot updates for security CVE
Setup[edit | edit source]
The software is mainly two components:
- elivepatch-client: Client to be run on the machines to be updated.
- elivepatch-server: Server in charge of building the livepatch modules.
The two use a RESTful API for receiving the kernel configuration and a source 'diff' and generate a livepatch module out of it using kpatch
Server setup[edit | edit source]
root #emerge --ask sys-apps/elivepatch-serverThis will install the init.d file under /etc/init.d/elivepatch and the conf.d under /etc/conf.d/elivepatch.
From the conf.d file you can change the elivepatch daemon user and permission (by default is root).
You can start elivepatch-server on machine startup with:
root #rc-config add elivepatch-server defaultThe machine will need to have enough space to build several kernels and the toolchains used to build the original kernel.
Client setup[edit | edit source]
root #emerge --ask sys-apps/elivepatch-clientThe client is as well a Python program.
Usage examples[edit | edit source]
One time livepatch build[edit | edit source]
root #elivepatch --config <file.config> --patch <example.patch> --url <elivepatch-server_url:elivepatch-server_port>The example.patch is a diff from the original kernel sources the file.config belongs to (the elivepatch-client figures out the kernel version from it).
The command will contact the elivepatch server and request a livepatch module matching the patch provided.
CVE livepatch[edit | edit source]
root #elivepatch --cve --kernel <kernel_version> --url <elivepatch-server-url:port>It will automatically produce a cve.patch from the CVE advisories for the current running kernel and request a livepatch module.
It could be used as a cron job command to keep an always-on machine up to date security-wise.
Limitations[edit | edit source]
Patch creation[edit | edit source]
elivepatch uses kpatch under the hood and the system has the following limitations:
- Patch that change data structure
- Change content of existing variable
- Add field to existing data structure
- Init code changes are incompatible with kpatch
- Header file changes
- Dealing with unexpected changed functions
- Removing references to static local variables
- Code removal
Toolchain pinning[edit | edit source]
The livepatch generation process needs a toolchain matching the one used to build the original kernel. Depending on the number of system to serve, this will require a large collection of gcc.
Security concerns[edit | edit source]
Automated live patching creation needs to trust the diff provided. It is advised to keep the process containerized. For this purpose Docker images are being worked on.
Background[edit | edit source]
This project is part of GSoC 2017 and the code is written by User:Alicef mentored by User:Gokturk
Written code:
- kpatch ebuild merged in the Gentoo official repository
- elivepatch client
- elivepatch server
- Official Gentoo repository elivepatch merge pull-request
Reports: